Working with heavy files and sharing them with multiple users is just a regular day at the office for media and entertainment teams. To ensure a seamless workflow and maintain high productivity levels, you need fast, reliable, and secure storage for your large media files, which is why an examination of SAN vs NAS can be especially useful for media pros.
Network attached storage (NAS) and storage area network (SAN) are storage architectures often used by video professionals. They both allow users to store and manage data in a centralized location while sharing it with multiple stakeholders but differ greatly in their approach.
Unsure which is best for your situation? Then this blog is for you. Read on to find out how both a NAS system and SAN storage work, and the advantages and disadvantages of each one.
Table of Contents
Secure File Sharing for Media Teams
MASV offers secure, reliable, and lightning-fast delivery of heavy media files.
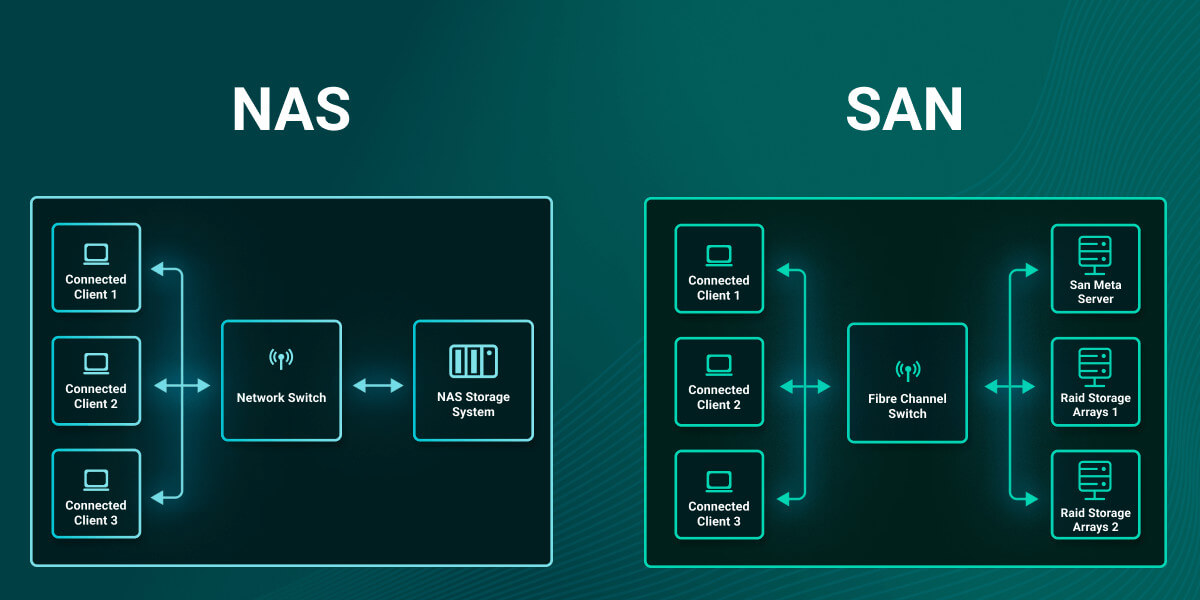
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
A NAS is an easy-to-set-up single storage device, or network node, that typically serves files over ethernet. NAS storage stores unstructured data, such as audio, video, and text files, in a centralized location that all devices on your network can access. A device such as a QNAP or Synology NAS is usually a box with multiple hard drives in a disk array called a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID).
When evaluating whether to go with a SAN vs NAS, keep in mind that because a NAS storage system is easy to set up, stores data on a local network, and provides file-level access, it’s best suited for at-home use, freelancers, and small to medium-sized businesses (SMEs) that require collaboration and file sharing between multiple users in multiple locations.
Use cases of NAS devices
For users who require general centralized data storage and file sharing and are unsure of whether to go with a SAN vs NAS, a NAS device can give them everything they need. It’s popular for home use where people within the household can access files such as photos, music, documents, and videos from any device within the home network.
NAS devices are also popular among those who work from home, such as freelance video editors or VFX artists.
💡 The capabilities of a NAS device can also support the file sharing needs of SMEs, such as post-production houses that need fast connected storage but don’t have the resources for a SAN.
Businesses often use a NAS device to enable their employees to store and access files in a centralized on-prem storage location, allowing for enhanced collaboration and reduced data duplication.
Pros of NAS for data storage
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Most suitable for unstructured data such as video and images.
- Easy to set up and deploy.
- Allows file sharing with offsite stakeholders.
- Sufficient for general file sharing in smaller environments.
- Automatic data recovery / backups to other devices and the cloud.
- Offers redundancy.
- Fast speeds.
Cons of NAS for data storage
- Limited scalability—dependent on the number of hard drives the device supports.
- Susceptible to interruptions and downtime due to its single point of failure.
- Typically not suitable for block level storage.
- Limited by network bandwidth.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
A SAN is a special high-speed network of multiple devices connected by a fibre channel that stores and provides access to large amounts of data, allowing the data to be centrally managed on a dedicated network segregated from the local area network (LAN). The separation of storage data transfers from other network traffic allows for greater performance speeds.
A SAN operates on the block level and consists of several disk arrays, switches, and servers, and is designed to handle data-intensive tasks that require very fast speeds.
When a server accesses the data on a SAN, it does so as if it were a local hard drive. As a result, operating systems recognize it as a locally attached hard drive rather than a shared network drive.
Given its high speeds, ability to handle larger amounts of data, and high tolerance to interruptions, a SAN storage area network is much more expensive and complex to set up than a NAS and requires administration by IT staff. This is why it’s best suited for large businesses and organizations carrying out high-performance enterprise-level applications.
Use cases of SAN technology
A SAN device is beneficial to organizations that handle large volumes of data and need their team members to work on multiple projects simultaneously. The more storage controllers you add, the faster the network.
💡 Generally speaking, SAN supports the enterprise storage needs of large businesses. These organizations produce, edit, and share high-res media files that can amount to hundreds of GBs and even TBs, which calls for the high throughput and low latency that SAN offers.
SAN technology is perfect for media and entertainment companies contemplating on whether to go with a SAN vs NAS, such as post-production studios, broadcast networks, animation and VFX studios, and creative agencies. When you have hundreds of video editors, colorists, and other collaborators who need to access tens of GBs per second of storage simultaneously, SAN allows you to do that without slowing down your network.
Pros of SAN for data storage
- Extremely fast speeds.
- Most suitable for structured data.
- Unaffected by network/LAN traffic.
- Highly scalable without interrupting the network.
- Highly redundant.
- Operates at the block level, providing raw storage that can be partitioned and formatted as needed.
- Strong data protection measures.
- Greater storage capacity.
Cons of SAN for data storage
- Complex to set up and deploy.
- High setup and operational costs.
- Need for skilled IT personnel to manage.
Boost Your Post-Production Workflow
MASV makes file sharing and file storage as easy as 1-2-3.
SAN vs NAS: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| SAN | NAS | |
| Method of data access | As if it were a local hard drive |
As if it were a network-attached drive |
| Type of storage | Block-level access | File-level access |
| Types of users | Large businesses | At-home use, individuals, freelancers, and SMEs |
| Use case |
Mission-critical and high-performance applications | Small environments, standard file sharing, and collaboration |
| Cost |
Expensive | Less expensive |
| Speed |
Extremely fast | Fast |
| Scalability |
Highly scalable | Limited scalability |
| Administration |
Requires skilled IT staff | Easy to set up and manage |
Is SAN or NAS Right for You?
SAN vs NAS: Which to go with?
NAS storage devices provide file-level storage accessible over a network and are cheaper and easier to set up. This makes them better suited to freelancers and SMEs.
- When it comes to sharing files, the solution with the fastest speeds and best performance is often the most attractive. But you have to strike a balance between performance and price given your budget. If you need fast speeds for standard file sharing and collaboration, NAS could be perfect for your organization or team.
- On the other hand, SAN is a specialized high-speed network that offers block level storage and separates storage traffic from other network traffic. It’s more expensive and complicated to set up and maintain, making it better suited to larger businesses. If you have the budget, need extremely fast speeds, and have dozens or hundreds of people accessing large files at the same time, SAN would be the best option.
Simplify File Sharing to Multiple Storage Destinations
Whether you’re using a network storage solution like SAN vs NAS, or cloud storage—or you’re using one or multiple storage options—you need a simple way to manage and ingest content into them all. And that’s where MASV comes in.
MASV Centralized Ingest offers a centralized, secure, and automated gateway for various cloud storage (including infrequently accessed storage types) and connected on-prem storage devices.
It’s a secure, unified, browser-based entry point to multiple storage destinations that simplifies content ingestion and helps cut down the configuration and management burden of multiple storage platforms. IT admins can easily connect multiple storage destinations through MASV’s centralized, browser-based interface, allowing project teams to automate media into shared storage using a user-friendly upload Portal.
Sign up for MASV today and start for free.
Reduce Storage Chaos
Automatically upload your files to your storage devices and networks.