Imagine you are trying to send a large file over the internet on a single Wi-Fi connection. For example, some raw camera footage weighing a couple hundred gigabytes. That delivery will take some time given the amount of data and your internet speed; the average US internet speed is under 50Mbps.
To get that file moving, you need faster internet speeds, which is where bonded internet connections can come in handy. And bonded internet is when two or more separate internet connections join to combine their speeds and create a single, much faster pipe.
It’s a popular method used to:
- Speed up file transfers
- Stabilize live streaming and gaming connections
- Smooth out playback of a video stream
But what is bonded internet exactly? How does it boost internet speed? And how is it different from other bonded technology like load balancing and failover?
I’ll answer all these questions and more below.
Table of Contents
Transfer Large Video Files
Send and receive large media assets over the cloud with MASV.
What is a Bonded Internet Connection?
Also known as channel bonding, broadband bonding, connection bonding, link bonding, ethernet bonding, or network interface card (NIC) bonding; a bonded internet connection is when you pair two or more internet sources together.
For example, you could channel bond 2Gbps ethernet with a 1Gbps 5G connection to create a single 3Gbps connection.
By combining two or more internet connections, you receive more bandwidth for a stable connection, experience lower latency, and have less chance of downtime, thanks to the redundancy of multiple connections.
What Connections Can be Bonded Together?
Pretty much any modern internet connection can be bonded with one another using the right setup, like the following:
-
Wi-Fi
-
Ethernet (fiber, cable, DSL, etc.)
-
LTE (4G)
-
5G
-
Satellite internet
-
Fixed wireless
Bonded Internet File Transfer
Sign-up for MASV and gain access to our exclusive Multiconnect channel bonding feature. Speed up large file uploads and downloads without any special hardware.
How to Combine Internet Connections for Faster Speeds?
Channel bonding will typically use a single IP address in order to establish a bonded connection for faster internet speeds via two methods: hardware and software.
- Hardware – Specialized networking hardware such as a bonding router, which can connect to multiple internet signals and bond them together. This approach, however, isn’t always realistic as bonding routers can be expensive, tough to configure, and require ongoing technical support.
- Software – Installing specialized channel bonding software on your computer or router. Some channel bonding software runs as a virtual private network (VPN) in the background and bonds all your web traffic. Others, like MASV Multiconnect, provide bonded internet to speed up upload and download speeds of large file transfers.
And no matter which approach you choose, perform a speed test before and after setting up your bonded connection. Otherwise, you’ll have no way of definitively knowing the difference.
Note: in both examples above, you also need multiple internet connections for bonding to be possible. You cannot connect two devices to the same Wi-Fi network and consider that channel bonding.
Is Bonded Internet the Same as Load Balancing?
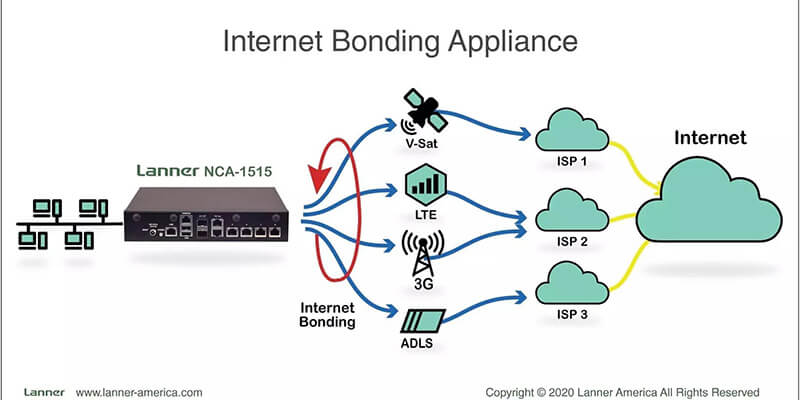
Source: Lanner America
Channel bonding is often confused with load balancing. Although they share similar qualities, the use case is not the same.
Whereas bonded internet combines multiple connections into a single fast line, load balancing uses multiple connections to distribute traffic more evenly across servers.
Load balancing ensures reliability and can improve overall network performance because it ensures no one server can be overwhelmed with traffic. It requires specific load-balancing routers (a router that can handle multiple WAN connections) or software such as a load-balancing VPN.
Unlike bonded internet, load balancing can’t provide a larger single pipe. That means it can’t speed up a single-socket connection for streaming, downloading, or file transfer applications.
Send Large Files (Anywhere in the World)
Whether you’re at-home, in an office, or on-location — MASV will deliver all your large media files.
What Happens if a Connection Goes Down (Failover)?
Another point of confusion is between channel bonding and failover.
Failover systems are another network configuration that uses multiple internet connections to ensure high uptime and availability. The difference is, failover uses these connections as a backup to the primary connection.
So, if one connection goes down, another one is ready to take its place. Failovers don’t improve speed or performance.
Automatic failovers, however, are a benefit of channel bonding. The very nature of a bonded internet connection means having a network of backups that can carry traffic if one network goes down.
Why is Bonded Internet Used (and Who is it For)?
Bonded internet is typically used by those who need faster download and upload speeds than their internet service providers can provide in a single pipe.
For the above reason, it’s popular in remote parts of the world with poor infrastructure and limited access to fast internet.
But bonded connections are also super handy for users who need an extra jolt of bandwidth and reliability, full-time or temporarily, under any circumstances. For example:
-
A creator who needs reliable internet when running a livestream
-
An editor who needs to receive a large multi-terabyte delivery of video files
-
An executive who requires a steady virtual conference stream for an important presentation
Why (and How) MASV Uses Bonded Internet
I mentioned two main ways of setting up a bonded internet connection: upgrading your hardware with an expensive bonding router or using specialized bonding software.
I also mentioned that most bonding software runs as a VPN on your computer or router and bonds all your internet traffic.
But MASV is different. MASV Multiconnect is specially designed for large file transfer and delivers uploads up to three times faster than a single connection.
It’s perfect for video pros working remotely or shooting on location who need to transfer footage quickly but without the hassle or added expense of setting up extra hardware or a subscription-based VPN.
MASV also provides advanced speed controls to users such as:
- Speed Limits – which enables users to set the maximum upload and download speed for each connection. Users can configure maximum speeds to correlate to specific times or days of the week.
- 10Gbps Optimization – our desktop app is tuned to handle a large influx of network speeds — up to 10Gbps. With that kind of speed, users can deliver a terabyte of data in under twenty minutes.
Wanna give it a try? Sign up and get free data to use each month, then download the MASV Desktop App to get started.
MASV File Transfer
Get the fastest, large file transfer service available today, MASV.