Compressing video files is often necessary when the size of the file exceeds the limit of a file transfer service or you need to conserve storage space.
Compressing a video file reduces its size, making it easier to share, manage, and store, albeit, with a loss in quality (depending on the compression technique used). If you cannot sacrifice video quality, luckily, you can use a large file transfer service like MASV which doesn’t require you to compress large video files.
Regardless, if you need to know how to make a video file smaller, read this guide. You’ll learn how to compress a video file. You’ll also learn the fundamentals like what is video compression exactly? The different types of compression, how to compress large video files, and the pros and cons of doing so.👇

How To Compress a Video
- What is Video Compression?
- The Pros and Cons of Compressing Video Files
- How Does Video Compression Work?
- What is a Video Codec?
- What are the Best Video Compression Formats?
- How to Compress a Video on Mac?
- How to Compress a Video on iPhone?
- How to Compress a Video on Android?
- How to Compress a Video on Windows?
- Popular Third-Party Compression Tools
- How to Send Uncompressed Video Files?
Need to Send Large Videos Now?
Send uncompressed file packages of unlimited size with MASV. Get started for free.
What is Video Compression?
In short, video compression is the act of reducing video file size by lowering its resolution and bitrate. This is done automatically by an algorithm, which parses the video file and searches for any data that can be removed without (hopefully) corrupting the overall file.
Compressing video files can be incredibly useful when sending raw footage or particularly large video files to collaborators, partners, and clients. It helps get around the often-frustrating file size limitations of many file transfer and email platforms.
Most file transfer services like WeTransfer, and Dropbox have strict file size limits, which force users to seek out compression in the first place.
The downside, however, is a loss in quality since video compression requires data to be deleted. Depending on the compression codec, that loss can be non-existent, minimal, or pretty noticeable.
Let’s examine the pros and cons of compression so you understand the tradeoff:
The Pros and Cons of Compressing Video Files
Pros ✅
- Reduce video file size to save on storage space and file transfer time.
- Reduce the processing strain on your computer when streaming/editing large video.
- Reduce overall network bandwidth usage which frees up the network for other users/tasks.
Cons ❌
- Compression can downgrade video and audio quality. This is especially noticeable if your viewers use a large screen (that pixelated or grainy look is the result of a compression artifact).
- Compressing video files takes time and can add hours to your turnaround time.
- File errors can crop up during the compression process; your recipients may not be able to open your compressed file immediately (if they don’t have the right software).
How to Send a Video That is Too Large?
MASV: fast, easy, and secure delivery of large video files.
How Does Video Compression Work?
Video compression augments the baked-in capture settings of a piece of footage by altering the following: resolution, bitrate, and encoding.
- Resolution is the number of pixels, typically represented by a horizontal x vertical measurement (1080p HD video, for example, has a resolution of 1920 x 1080).
- Bitrate measures how much information is transmitted for each second of video. It’s usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps).
- Encoding consists of both the codec along with its container or file type (such as AVI or MP4).
There are other factors that help determine video file size including video length and frame rate (measured by frames per second, or FPS).
A good rule of thumb is: the stronger the compression, the more it impacts the video.
It’s why some video disciplines, like colorists prefer to work with the original file (or files with minimal compression). A video compression algorithm might take out shades of the same color to save space, which in turn, affects the color grading process.
💡 Read More: Gigabyte vs Gibibyte – What’s the Difference?
Send Unlimited Video Files With MASV
Easy sign-up. No IT support necessary.
What is a Video Codec?
Codecs are the algorithms used by various file formats to store video and audio data. Codec stands for compression/decompression and several types of video codecs exist including H.264, ProRes, or DNxHD. These codecs are then stored in a specific file format, or wrapper, such as .MOV, .MP4, .AVI etc.
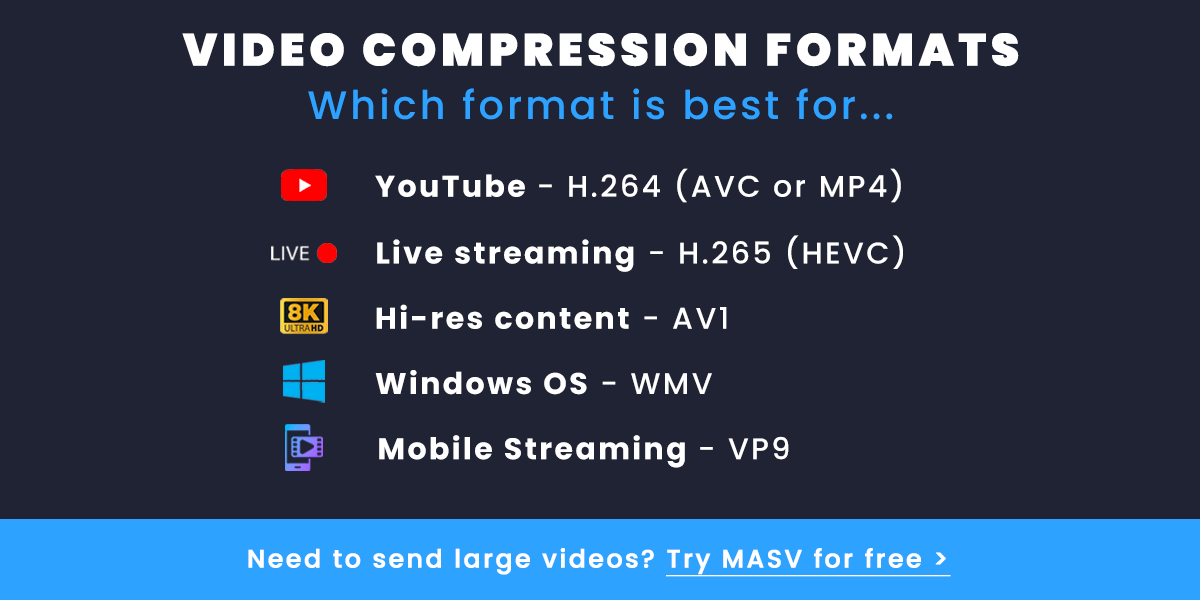
What are the Best Video Compression Formats?
Delivery Codecs (for streaming/broadcast):
Delivery codecs are codecs used to compress video for broadcasting. Increasingly, delivery codecs are evolving to support high resolution streaming over the internet, across different devices. For example, H.265 offers encoding for 8K footage.
- H.264 (AVC or MPEG-4): best for uploading to YouTube
- H.265 (HEVC): best for live streaming since it further reduces the file size and requires less bandwidth
- AV1: for streaming high-resolution 4K or 8K content
- WMV: compatible with all Windows operating systems, making it super convenient on this OS
- VP9: for streaming from low-end devices like smartphones because it can cut the bit rate in half without affecting quality
Intermediate Codecs (for editing):
Intermediate codecs are codecs to be used when editing. These codecs make it easier to edit with large footage by reducing the processing strain on your computer. An example of this is ProRes, which Apple introduced as a recording format starting with the iPhone 13.
- ProRes
- DNxHD
- Blackmagic Raw
- GoPro Cineform
- Grass Valley HQX
Most video codecs perform “lossy” compression in that they always throw out some data in order to compress the file and make it smaller — hence the video quality issues related to compression that we mentioned earlier.
Growing file Codecs (for live events):
Growing files can be worked with while they’re still recording data. For example, an editor would access a growing file to create highlights clips from a sports broadcast that is still airing. In fact a single growing MXF file can be up to 12 hours long!
File formats that support growing files include MXF files and QuickTime .MOV files. The following codecs are most often used when recording and editing growing files:
- ProRes
- H.264
- XAVC
- DNxHD / DNxHR
- XDCAM HD / XDCAM EX
- AVC-Intra
💡 Read More: Understanding Video File Formats and Use Cases
Make the Switch to MASV
Give your team more time for big picture thinking.
How to Compress a Video on Mac?
Now, let’s look at how to compress a video file on different devices. First up: MacOS.
If you’re on a Mac, you actually have three different ways to compress a large video. You have two built-in options in iMovie and Quicktime, which is very convenient. Or, you can use a third-party editing tool like Final Cut Pro, Adobe Premiere Pro, or DaVinci Resolve.
How to Compress a Video on Mac Using Quicktime?
1. From the Quicktime menu, select “Open File” to open the video file you’re going to compress.
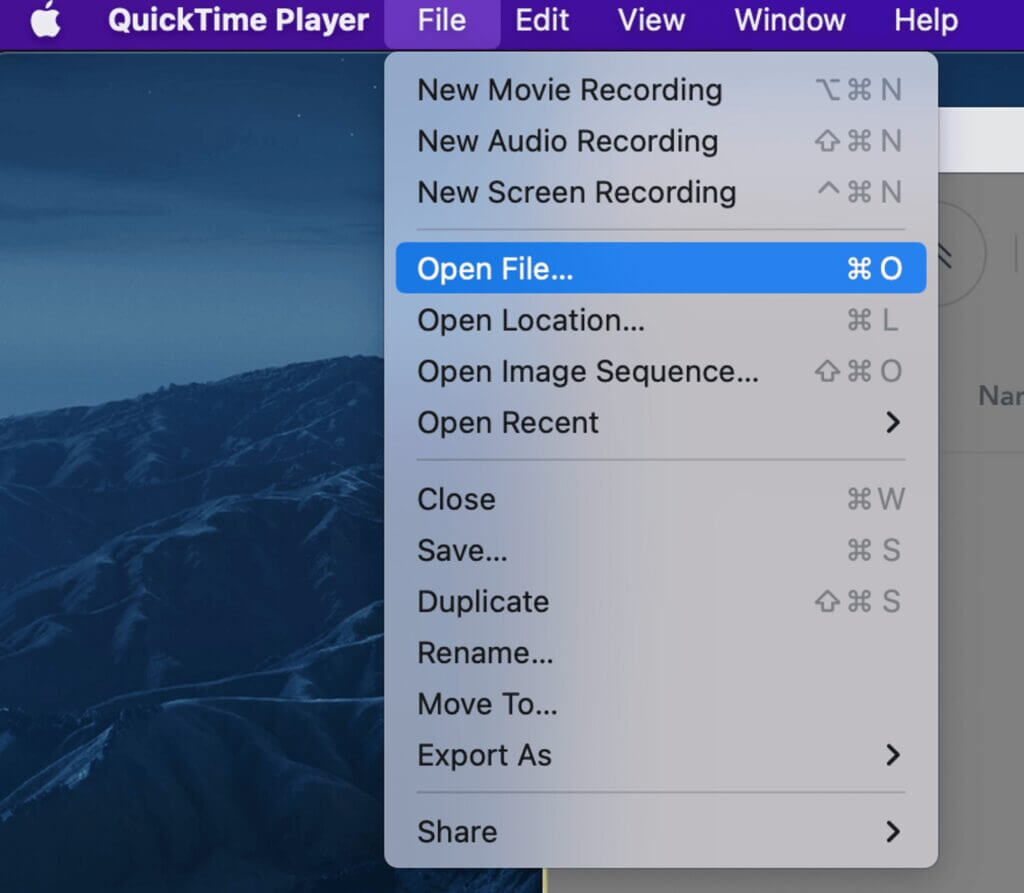
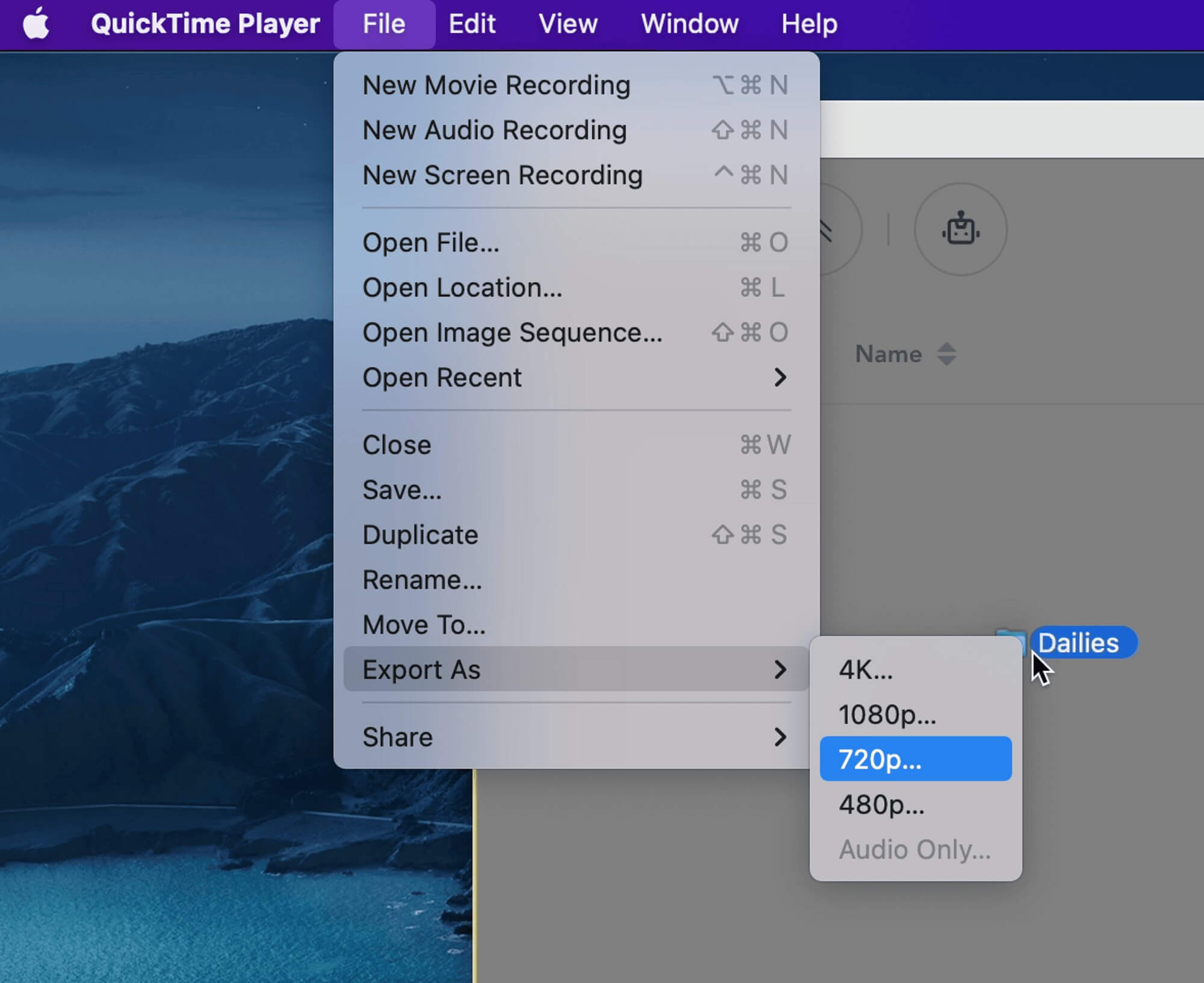
2. Next, go to File > Export As > Choose a resolution
How to Compress a Video on Mac Using iMovie?
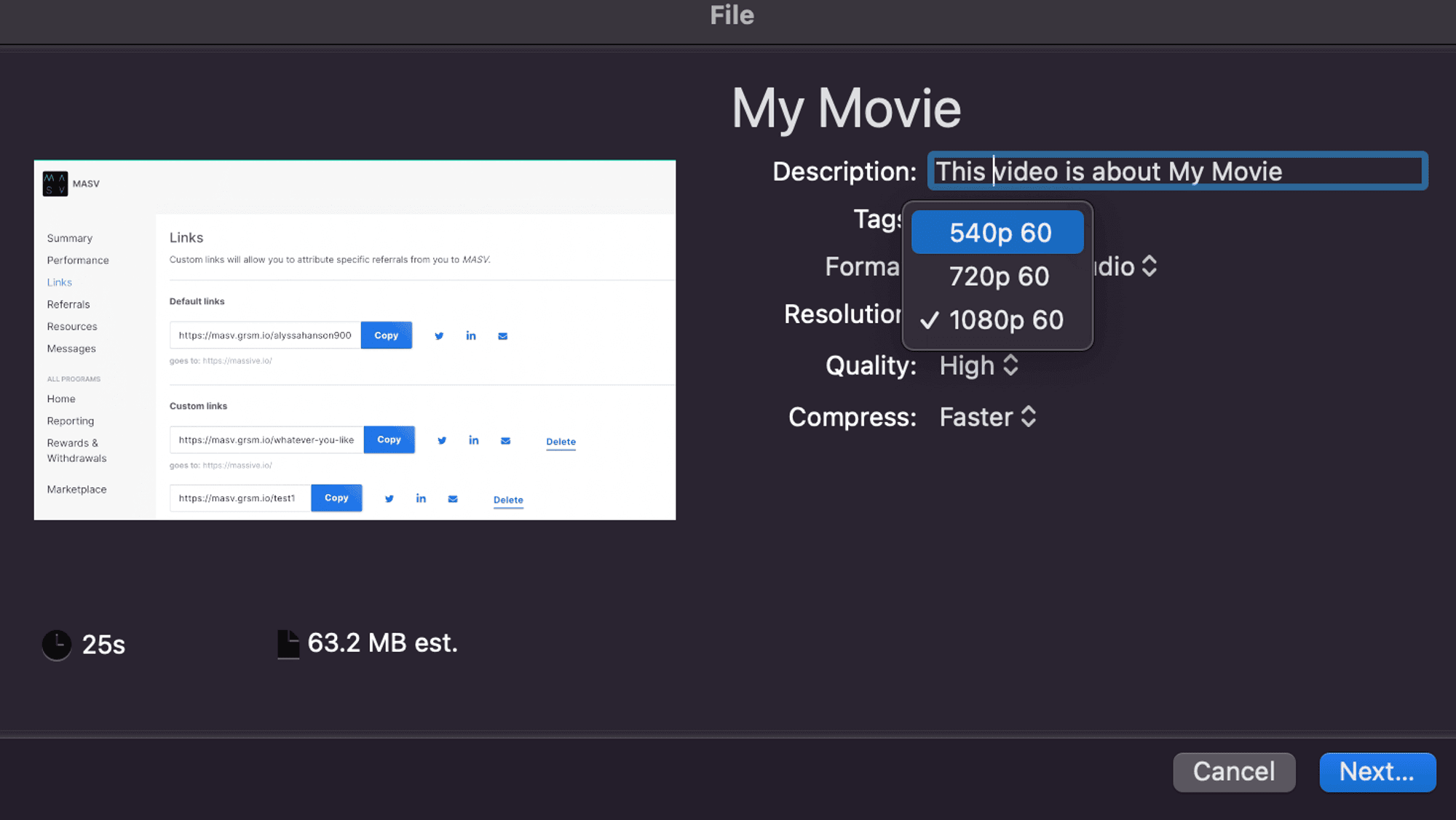
1. With your video file open in iMovie, Go to File > Share > File
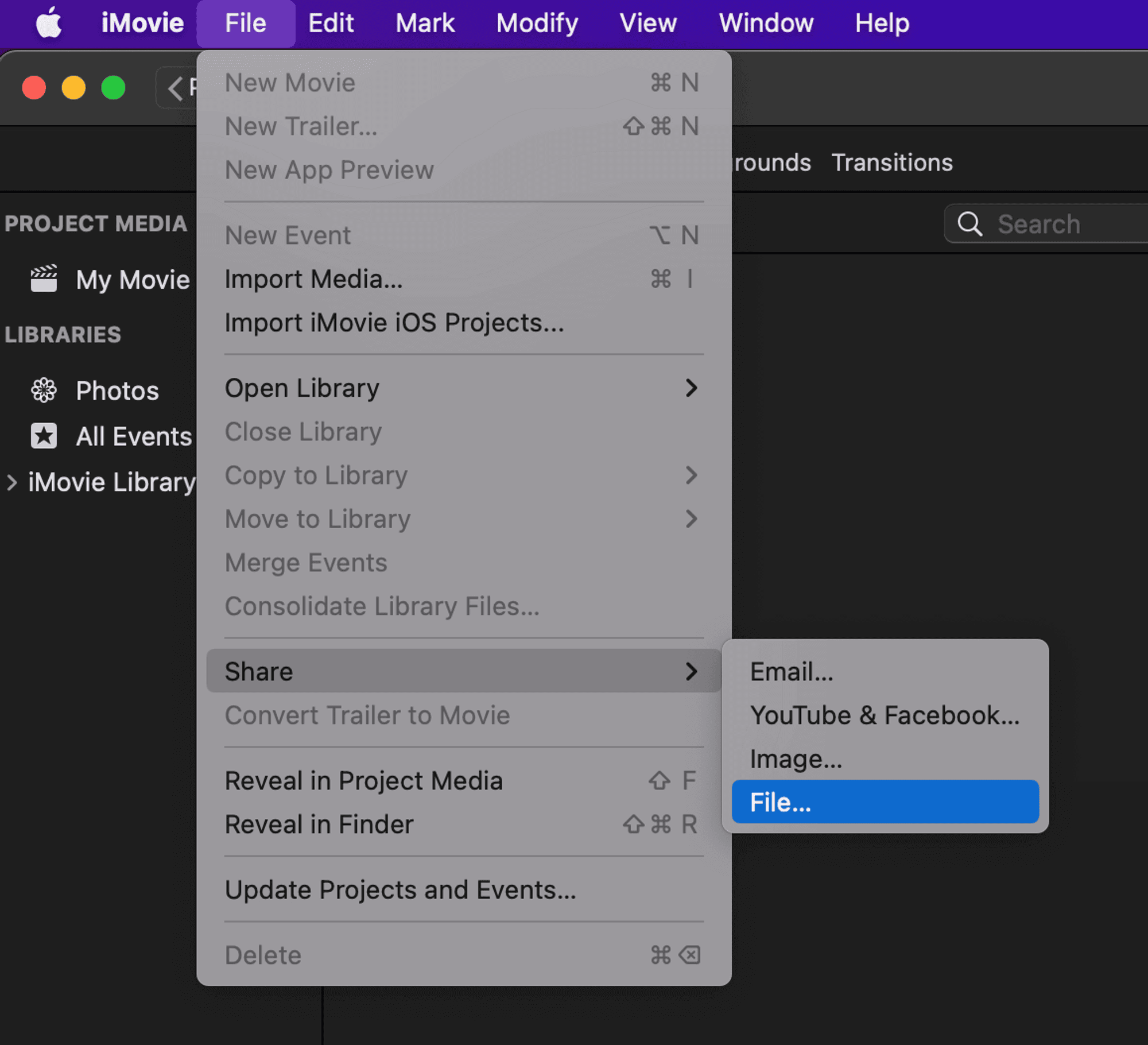
2. Choose your desired resolution quality
Need to Send Large Videos Now?
Send uncompressed file packages of unlimited size with MASV. Try it free.
How to Compress a Video on iPhone?
- Before recording a video on your iPhone, go to Settings > Camera > Record Video > reduce the resolution and frame rate. This won’t compress any existing videos but it will ensure any new videos are smaller.
- Use a video compression app like Video compressor.
How to Compress a Video on Android?
- Open up your native Camera app > Select the gear icon in the top left corner > reduce the resolution and frame rate.
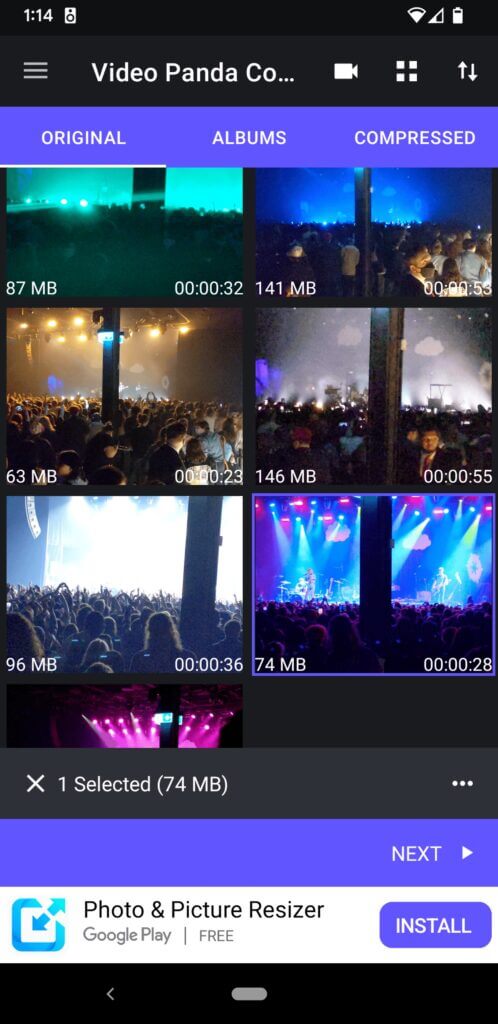
- Use a video compression app like Panda Video Compressor & Video Resizer.
1. With the app open, select the video you want to compress, and click “next”
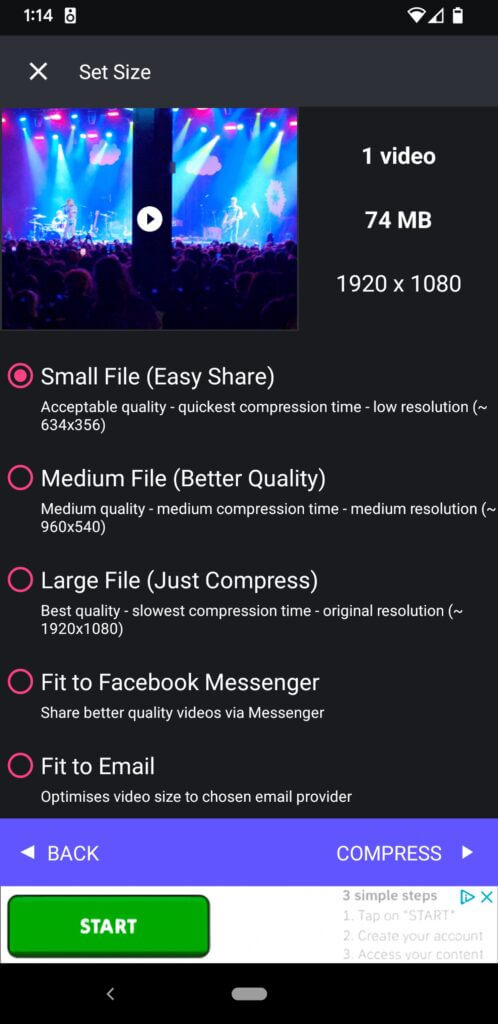
2. Choose your desired compression settings. You can choose from small, medium, large, or choose settings that are best for email or messaging.
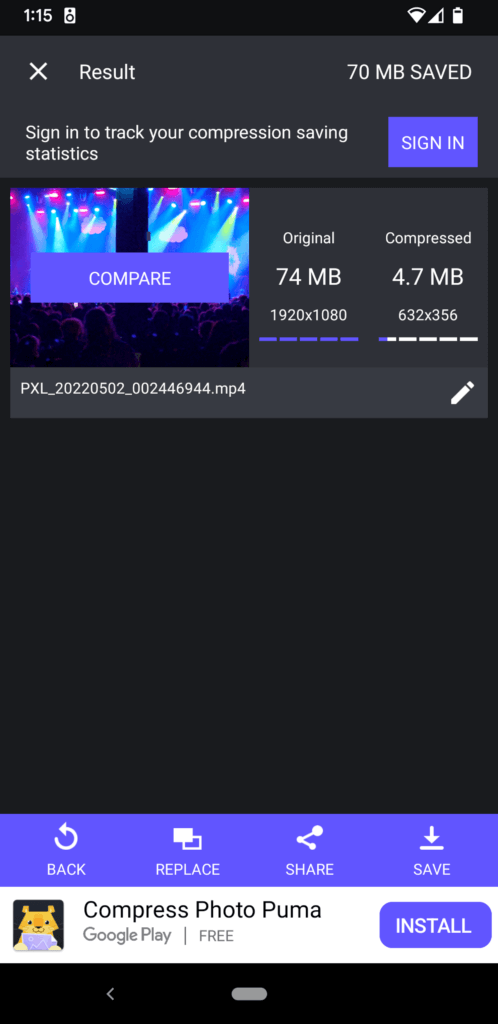
3. Save your compressed video to your device, or share it with someone else.
How to Compress a Video on Windows?
Windows machines come with a native Video Editor app, which is your best to compress video files on Windows.
- Launch Video Editor > Start a new project > Add video file > Click ‘Finish Video’ > choose video resolution.
You can also use Clipchamp which is a video editor available on browser — or as an exclusive desktop app for Windows devices. Microsoft acquired Clipchamp in 2021 and has since introduced desktop compatibility.
- Open Clipchamp on browser/desktop > add your video > export > choose video resolution
Note, both Video Editor and Clipchamp only offer 1080p as their max resolutions.
Popular Third-Party Compression Tools
Below are some other compression tools you can use, which aren’t device-specific.
- VLC Media Player
- VideoProc Converter
- Handbrake
- Inshot, Capcut, Splice, and other popular mobile video editing apps.
How to Send Uncompressed Video Files?
Here’s the thing about compression: if your video quality matters, don’t do it.
Video pros who need to send content at maximum resolution or in RAW will find that MASV can deliver terabytes of data (including file packages of unlimited size) from the browser or the insanely fast and reliable MASV app.
- MASV has a network of 300+ servers in global locations, which means you can send and receive files on a worldwide scale.
- MASV maintains your folder structure so you don’t have to spend the extra time zipping files prior to upload (that avoids corruption too).
- All MASV transfers are encrypted at in-flight and at-rest.
- All transfers also resume where they left off in the event of a network failure.
- Signing up for MASV also means gaining access to file transfer automations, direct-to-cloud storage, internet bonding, and our free desktop app which is faster than our browser instance.
It’s free to get started. Our free account gives you data every month so you can test our speed and see the MASV difference for yourself.
MASV File Transfer
Get started with the fastest, large file transfer service available today, MASV.